Physics and Mathematics
Modulus Function
1. Concept Overview
The modulus function helps us understand the idea of distance on the number line.
It always gives a non-negative value, regardless of whether the input is positive or negative.
Key idea:
Modulus removes the sign of a number but keeps its magnitude.
2. Definition of Modulus Function
The modulus function is defined as:
[f(x)=|x|]
which means
[|x| = x] if [x ≥ 0]
[|x| = −x] if [x < 0]
3. Meaning of Modulus
- [|x|] represents the distance of x from 0 on the number line
- Distance is never negative
Examples:
[|5| = 5]
[|−5| = 5]
4. Domain and Range
Domain:
All real numbers
[(−∞,∞)]
Range:
All non-negative real numbers
[[0,∞)]
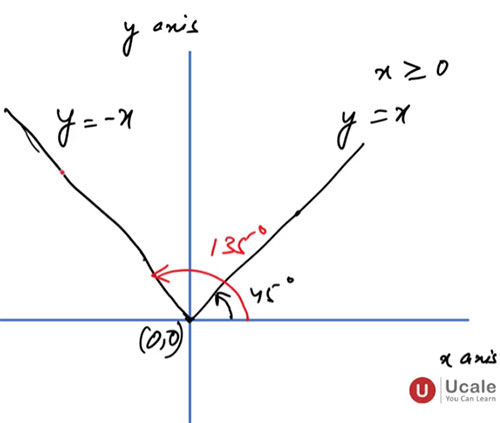
5. Graph of Modulus Function
- Graph of [y=|x|] is V-shaped
- Vertex at the origin [(0,0)]
- Symmetric about the y-axis
- Continuous everywhere
6. Properties of Modulus Function
- [|x| ≥ 0]
- [|x| = 0 ⇔ x = 0]
- [|−x| = |x|] (even function)
- [|x| ≥ x] and [|x| ≥ −x]
7. Piecewise Nature
Modulus function is a piecewise-defined function because its rule changes based on the value of [x].
8. Examples with Solutions
Example 1. Find the value of [|−7|].
Solution:
Since [−7 < 0],
[|−7| = −(−7) = 7]
Example 2. Evaluate [|5 − 9|].
Solution:
[5 − 9 = −4]
So, [|5 − 9| = 4]
Example 3. Simplify [|x|] for [x = −3].
Solution:
Since [x < 0],
[|x| = −x = 3]
Example 4. Write [|x|] as a piecewise function.
Solution:
[|x| = x] for [x ≥ 0]
[|x| = −x] for [x < 0]
Example 5. Find the range of [f(x)=|x|].
Solution:
Since modulus is never negative,
Range = [[0,∞)]
9. Conceptual Questions with Solutions
1. What does modulus of a number represent?
It represents the distance of the number from zero on the number line.
2. Why is modulus always non-negative?
Because distance cannot be negative.
3. Is [|−x|] equal to [|x|]?
Yes, because both represent the same distance from zero.
4. What is the domain of modulus function?
The domain is all real numbers.
5. What is the range of modulus function?
The range is all non-negative real numbers.
6. Why is modulus function piecewise?
Because it follows different rules for positive and negative inputs.
7. Is modulus function continuous?
Yes, it is continuous everywhere.
8. Is modulus function one–one?
No, because [|x| = |−x|].
9. Is modulus function even?
Yes, because [f(−x)=f(x)].
10. Where does graph of modulus function meet x-axis?
At the origin only.
11. Does modulus function have an inverse?
No, because it is not one–one.
12. Why is graph symmetric about y-axis?
Because values at [x] and [−x] are equal.
13. Can modulus function be negative?
No. It is never negative.
14. What is [|0|]?
[|0| = 0].
15. Why is modulus function important?
It helps in studying distance, inequalities, and graphs.
10. FAQ / Common Misconceptions
1. [|x| = x] for all x.
False. It is true only when x ≥ 0.
2. Modulus can be negative.
False. It is always non-negative.
3. Modulus function is one–one.
False. It is many–one.
4. Modulus removes value.
False. It removes only the sign.
5. Domain is only positive numbers.
False. Domain is all real numbers.
6. Graph is a straight line.
False. It is V-shaped.
7. [|x| = 0] for many x.
False. Only at x = 0.
8. Modulus function has inverse.
False. It is not invertible.
9. Modulus is discontinuous.
False. It is continuous everywhere.
10. Modulus is not useful.
False. It is very important in mathematics and physics.
11. Practice Questions with Step-by-Step Solutions
Question 1. Find the value of [|−12|].
Step-by-Step Solution:
[−12 < 0]
[|−12| = −(−12)]
Conclusion:
[|−12| = 12]
Question 2. Evaluate [|7 − 15|].
Step-by-Step Solution:
[7 − 15 = −8]
Take modulus of [−8]
Conclusion:
[|7 − 15| = 8]
Question 3. Find [f(−4)] if [f(x)=|x|].
Step-by-Step Solution:
Substitute [x = −4]
Since input is negative, use [−x]
Conclusion:
[f(−4) = 4]
Question 4. Write [|x − 2|] as a piecewise function.
Step-by-Step Solution:
Consider when [x − 2 ≥ 0] ⇒ [x ≥ 2]
Consider when [x − 2 < 0] ⇒ [x < 2]
Conclusion:
[|x − 2| = x − 2] for [x ≥ 2]
[|x − 2| = 2 − x] for [x < 2]
Question 5. Find the range of [f(x)=|x−3|].
Step-by-Step Solution:
Modulus output is never negative
Minimum value occurs at [x = 3]
Conclusion:
Range = [[0,∞)]
Question 6. Solve [|x| = 6].
Step-by-Step Solution:
[|x| = 6] implies distance from zero is 6
So, [x = 6] or [x = −6]
Conclusion:
Solution set = [{−6,6}]
Question 7. Find the domain of [f(x)=|x+5|].
Step-by-Step Solution:
Modulus is defined for all real numbers
Conclusion:
Domain = [(−∞,∞)]
Question 8. Find the minimum value of [|x−4|].
Step-by-Step Solution:
Modulus is minimum when expression inside is zero
Set [x−4 = 0]
Conclusion:
Minimum value = 0
Question 9. Is the function [f(x)=|x|] one–one?
Step-by-Step Solution:
[f(2)=2] and [f(−2)=2]
Different inputs give same output
Conclusion:
Function is not one–one
Question 10. Is the modulus function even?
Step-by-Step Solution:
Check [f(−x)]
[|−x| = |x|]
Conclusion:
Modulus function is even