Physics and Mathematics
Constant Function
1. Concept Overview
A constant function is a function in which the output remains the same for every input.
No matter what value of [x] we choose, the value of the function does not change.
2. Definition of Constant Function
A function [f] is called a constant function if
[f(x)=c], where [c] is a constant real number.
Here:
- is the independent variable
- [c] is a fixed number
3. Examples of Constant Function
- [f(x)=5]
- [g(x)=−3]
- [h(x)=0]
In all cases, the output is independent of x.
4. Domain and Range of Constant Function
Domain:
The domain of a constant function is usually all real numbers, unless specified otherwise.
Range:
The range consists of only one value, i.e. [{c}].
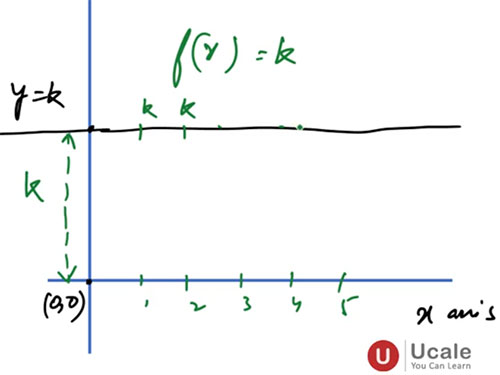
5. Graph of a Constant Function
The graph of [f(x)=c] is:
- a horizontal straight line
- parallel to the x-axis
- passing through the point [(0,c)]
6. Nature of Constant Function
A constant function is:
- many–one
- not one–one
- continuous everywhere
- neither increasing nor decreasing
7. Important Observations
- Output does not depend on input
- Slope of the graph is zero
- Derivative of a constant function is zero
- Inverse of a constant function does not exist
8. Conceptual Questions with Solutions
1. Why is it called a constant function?
Because the value of the function remains constant for all inputs.
2. Is [f(x)=3] a function?
Yes. Each input has exactly one output, which satisfies the definition of a function.
3. Why is a constant function many–one?
Because many different inputs give the same output.
4. Can a constant function be one–one?
No. A one–one function requires distinct outputs for distinct inputs.
5. What is the range of a constant function?
The range consists of only one element, the constant value [c].
6. Is the constant function continuous?
Yes. It is continuous everywhere on the real line.
7. Why is its graph parallel to x-axis?
Because the y-value does not change as [x] changes.
8. What is the slope of a constant function?
The slope of a constant function is zero.
9. Can the constant function be increasing?
No. Since the output is unchanged, it is neither increasing nor decreasing.
10. Is [f(x)=0] also a constant function?
Yes. Zero is also a constant value.
11. Does a constant function have an inverse?
No. It is not one–one, so its inverse does not exist.
12. Can domain of a constant function be restricted?
Yes. The domain can be restricted if specified.
13. Is a constant function polynomial?
Yes. It is a polynomial of degree zero.
14. Why is derivative of constant zero?
Because there is no change in output with respect to input.
15. Where are constant functions used?
They are used to represent fixed quantities in real-life situations.
9. FAQ / Common Misconceptions
1. A constant function is not a function.
False. It satisfies the definition of a function.
2. Constant function is one–one.
False. It is many–one.
3. Its graph is vertical.
False. Its graph is horizontal.
4. Range of constant function is all real numbers.
False. The range has only one value.
5. Constant function is discontinuous.
False. It is continuous everywhere.
6. Zero function is different from constant function.
False. It is a special case of constant function.
7. Constant functions have inverse.
False. They are not invertible.
8. Degree of constant polynomial is one.
False. It is of degree zero.
9. Constant function depends on x.
False. It is independent of x.
10. Constant function is increasing.
False. It is neither increasing nor decreasing.
10. Practice Questions with Step-by-Step Solutions
Question 1.
Find the domain and range of [f(x)=7].
Step-by-Step Solution:
- The function is defined for all real x.
- Output is always [7].
Conclusion:
Domain = [R]
Range = [{7}]
Question 2.
State whether [f(x)=−4] is one–one or many–one.
Step-by-Step Solution:
- All inputs give the same output.
- Hence it is many–one.
Conclusion:
The function is many–one.
Question 3.
Draw the graph of [f(x)=2].
Step-by-Step Solution:
- Output is always [2].
- Plot points like [(0,2)], [(1,2)], [(−1,2)].
- Join them to get a horizontal line.
Conclusion:
Graph is a horizontal line parallel to x-axis.
Question 4.
Is the function [f(x)=0] increasing, decreasing, or constant?
Step-by-Step Solution:
- Output remains unchanged.
- Hence it is constant.
Conclusion:
The function is constant.
Question 5.
Find [f′(x)] if [f(x)=9].
Step-by-Step Solution:
- Derivative of a constant is zero.
Conclusion:
[f′(x)=0]