Class 11th Physics Gravitation
Law of Gravitation
Earth's Gravitation
Gravitational Field and Potential
Satellite in Orbit
Kepler's Law of Planetary Motion
Upgrade to get full access
Kumar Rohan
Physics and Mathematics
Effect of Altitude on Acceleration due to Gravity
The value of acceleration due to gravity changes with height (i.e. altitude), depth or shape of the earth and rotation of the earth about its own axis. Suppose, if the mass of the earth is M, radius R with center at O. The acceleration due to gravity at a point A on the surface of earth is g.
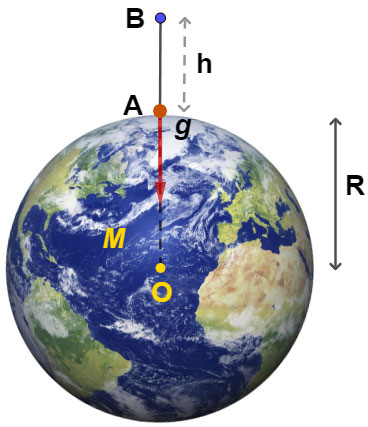
The acceleration due to gravity at a point B at an altitude of h above the earth surface is given by
$ \displaystyle {g}’=g\left( {1-\dfrac{{2h}}{R}} \right)$
The above value shows that as the height h increases the value of acceleration due to gravity $\displaystyle {{g}’}$ decreases. It is due to this reason that the value of acceleration due to gravity is less at mountains than in plains.