Physics and Mathematics
Newton’s First Law Defines Inertia
1. Concept Overview
Newton’s First Law of Motion states that an object remains in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force.
This law introduces the concept of inertia — the natural tendency of objects to resist a change in their state of motion.
Inertia is a property of matter that depends on mass. Greater the mass, greater the inertia.
2. Types of Inertia
There are three types of inertia:
| Type of Inertia | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Inertia of Rest | Tendency of a body to remain at rest unless acted upon by a force. | A passenger moves backward when a bus starts suddenly. |
| Inertia of Motion | Tendency of a moving body to continue moving unless stopped by a force. | A passenger moves forward when a moving bus stops suddenly. |
| Inertia of Direction | Tendency of a body to resist change in direction. | When a car takes a sharp turn, passengers tend to lean sideways. |
3. Relation Between Inertia and Mass
- The inertia of an object is directly proportional to its mass.
A heavy truck has more inertia than a bicycle; hence, it is harder to change its motion.
4. Real-Life Examples
- A coin placed on a card over a glass falls into the glass when the card is flicked away.
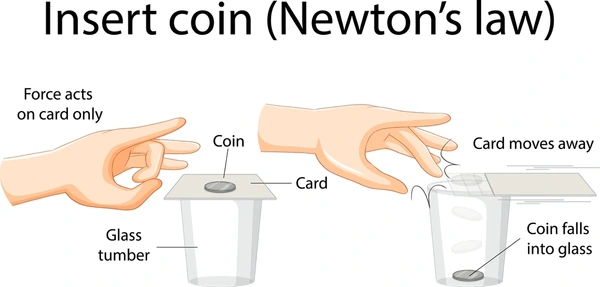
- Dust falls off a carpet when it is beaten.
- A person leans backward when a stationary bus suddenly starts.
- The upper part of the body tends to move forward when a moving vehicle stops suddenly.
5. Practice Questions (With Solutions)
Q1. Why does a passenger move backward when a bus starts suddenly?
Solution: Due to the inertia of rest, the passenger’s body tends to remain at rest even though the bus moves forward suddenly.
Q2. Explain why dust comes out of a carpet when it is beaten.
Solution: When the carpet is beaten, the carpet moves but the dust particles tend to remain at rest (inertia of rest) and thus get separated.
Q3. Why does a cyclist lean inward while taking a turn?
Solution: To counter the inertia of direction and prevent falling outward due to the change in motion’s direction.
Q4. Why does a ball rolling on the ground stop after some time?
Solution: Because of external forces like friction and air resistance acting on it, opposing its motion.
Q5. Why is it difficult to push a car than a bicycle?
Solution: A car has greater mass and hence greater inertia.
Q6. A truck and a car moving at the same speed apply brakes simultaneously. Which one will stop first?
Solution: The car will stop first because it has less mass (less inertia of motion).
Q7. Why do you feel a jerk when a moving lift stops suddenly?
Solution: Due to inertia of motion, your body tries to continue moving downward even when the lift stops.
6. Conceptual Questions
1. What does inertia depend upon?
Inertia depends on the mass of an object. More mass means more inertia.
2. Does a heavier body always have greater inertia?
Yes, for the same material and shape, a heavier body has greater inertia.
3. Why can’t we change the motion of a heavy body easily?
Because its high inertia resists any change in its state of motion.
4. Is inertia a force?
No, inertia is not a force. It is a property of matter.
5. If no force acts on a moving object, will it stop?
No, it will continue moving with the same speed in a straight line.
6. Can inertia be measured?
Not directly, but it can be compared through mass.
7. Does a rolling ball have inertia?
Yes, it has inertia of motion.
8. Does inertia apply to liquids and gases?
Yes, all matter (solid, liquid, or gas) possesses inertia.
9. Why is it easier to move an empty trolley than a loaded one?
Because the loaded trolley has greater mass and hence greater inertia.
10. Can an object have both inertia of rest and motion simultaneously?
No, at a given moment, an object can either resist rest or motion, not both.
7. FAQs / Common Misconceptions
1. Is inertia the same as momentum?
No. Inertia is a property of matter, while momentum depends on both mass and velocity.
2. If an object is heavy, does it mean it moves faster?
No. Heaviness (mass) increases inertia but not speed.
3. Can we see inertia?
No. We can only observe its effects when motion changes.
4. Is inertia caused by gravity?
No. Inertia exists even in space where there’s no gravity.
5. If no force acts, does every object eventually stop?
No. Without external forces (like friction), an object will continue moving indefinitely.