Physics and Mathematics
Signum Function
1. Concept Overview
The signum function tells us the sign of a real number.
It answers a very simple question:
Is the number positive, negative, or zero?
2. Definition of Signum Function
The signum function is denoted by [sgn(x)] and defined as:
[sgn(x) = −1] if [x < 0]
[sgn(x) = 0] if [x = 0]
[sgn(x) = 1] if [x > 0]
3. Relation Between Modulus and Signum
For [x ≠ 0],
[sgn(x) = \dfrac{x}{|x|}]
This shows that:
- Modulus gives the magnitude
- Signum gives the direction
4. Domain and Range
Domain:
All real numbers
[(−∞,∞)]
Range:
Only three values:
[{−1, 0, 1}]
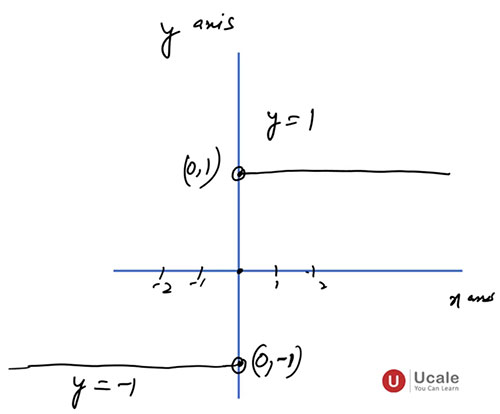
5. Graph of Signum Function
- Horizontal line at [y = 1] for [x > 0]
- Horizontal line at [y = −1] for [x < 0]
- A single point at [(0,0)]
- Discontinuous at x = 0
6. Properties of Signum Function
- [|sgn(x)| ≤ 1]
- [sgn(−x) = −sgn(x)] (odd function)
- [sgn(x)] gives only the sign, not magnitude
- [x = |x|·sgn(x)]
7. Examples with Solutions
Example 1. Find the value of [sgn(−9)].
Solution:
Since [−9 < 0], the signum function gives −1.
So, [sgn(−9) = −1]
Example 2. Find the value of [sgn(0)].
Solution:
At zero, signum function is defined as 0.
So, [sgn(0) = 0]
Example 3. Find the value of [sgn(15)].
Solution:
Since [15 > 0], the signum function gives 1.
So, [sgn(15) = 1]
Example 4. Express [sgn(x)] using modulus for [x ≠ 0].
Solution:
For [x ≠ 0],
[sgn(x) = \dfrac{x}{|x|}]
Example 5. Verify [x = |x|·sgn(x)] for [x = −6].
Solution:
[|−6| = 6] and [sgn(−6) = −1]
[|x|·sgn(x) = 6 × (−1) = −6]
Hence, verified.
8. Conceptual Questions with Solutions
1. What is the purpose of the signum function?
It tells whether a number is positive, negative, or zero.
2. What is the value of [sgn(0)]?
The value is 0.
3. What values can signum function take?
Only −1, 0, and 1.
4. Is signum function defined at zero?
Yes, and its value is 0.
5. Why is signum function discontinuous?
Because the left-hand and right-hand limits at zero are different.
6. Is signum function odd?
Yes, because [sgn(−x) = −sgn(x)].
7. What is the domain of signum function?
The domain is all real numbers.
8. What is the range of signum function?
The range is {−1, 0, 1}.
9. How is signum related to modulus?
By the relation [sgn(x)=x/|x|] for [x ≠ 0].
10. Does signum function give magnitude?
No, it gives only the sign.
11. What is the value of [sgn(−5)]?
Since the number is negative, the value is −1.
12. What is the value of [sgn(8)]?
Since the number is positive, the value is 1.
13. Is signum function one–one?
No, because many inputs give the same output.
14. Can signum function be represented using modulus?
Yes, using [x = |x|·sgn(x)].
15. Why is signum function important?
It is useful in studying piecewise functions and graphs.
9. FAQ / Common Misconceptions
1. Signum function gives the value of x.
False. It gives only the sign of x.
2. [sgn(0)=1]
False. [sgn(0)=0].
3. Signum function is continuous.
False. It is discontinuous at x = 0.
4. Range is all real numbers.
False. Range is only {−1,0,1}.
5. Signum function is even.
False. It is odd.
6. Signum is undefined at zero.
False. It is defined at zero.
7. [sgn(x)=|x|/x]
False. Correct relation is [sgn(x)=x/|x|].
8. Signum gives magnitude.
False. It gives only the sign.
9. Signum function has inverse.
False. It is not invertible.
10. Signum is not useful.
False. It is very useful in mathematics.
10. Practice Questions with Step-by-Step Solutions
Question 1. Find the value of [sgn(−12)].
Step-by-Step Solution:
Since [−12 < 0], the number is negative.
For negative numbers, [sgn(x) = −1].
Conclusion:
[sgn(−12) = −1]
Question 2. Find the value of [sgn(7)].
Step-by-Step Solution:
Since [7 > 0], the number is positive.
For positive numbers, [sgn(x) = 1].
Conclusion:
[sgn(7) = 1]
Question 3. Find the value of [sgn(0)].
Step-by-Step Solution:
The signum function is defined at zero.
Its value at zero is 0.
Conclusion:
[sgn(0) = 0]
Question 4. Evaluate [sgn(5 − 9)].
Step-by-Step Solution:
Simplify inside: [5 − 9 = −4].
Since the result is negative, signum value is −1.
Conclusion:
[sgn(5 − 9) = −1]
Question 5. Express [sgn(x)] in terms of modulus for [x ≠ 0].
Step-by-Step Solution:
Use the relation between signum and modulus.
Conclusion:
[sgn(x) = \dfrac{x}{|x|}]
Question 6. Verify that [sgn(−x) = −sgn(x)] for [x = 4].
Step-by-Step Solution:
LHS: [sgn(−4) = −1].
RHS: [−sgn(4) = −1].
Conclusion:
LHS = RHS, hence verified.
Question 7. Find the value of [|sgn(−8)|].
Step-by-Step Solution:
[sgn(−8) = −1].
Take modulus: [|−1| = 1].
Conclusion:
[|sgn(−8)| = 1]
Question 8. Find the value of [sgn(3) + sgn(−3)].
Step-by-Step Solution:
[sgn(3) = 1].
[sgn(−3) = −1].
Conclusion:
[sgn(3) + sgn(−3) = 0]
Question 9. Find the domain of [sgn(x)].
Step-by-Step Solution:
Signum function is defined for all real numbers.
Conclusion:
Domain = [(−∞,∞)]
Question 10. Is the signum function one–one?
Step-by-Step Solution:
Many values of x give the same output.
Example: [sgn(2) = sgn(5) = 1].
Conclusion:
Signum function is not one–one.